Biometrids - Decentralised and Anonymous ID by Facial Recognition on the Blockchain.
A facial recognition system is a computer application capable of identifying or verifying a person from a digital image or a video frame from a video source. One way to do this is by comparing the selected facial features of the image and a database of faces. It is normally used in security systems and can be compared with other biometric data, such as fingerprint or eye iris recognition systems. Recently, it has also become popular as a commercial identification and marketing tool. Techniques for face acquisition Some facial recognition algorithms identify facial features by extracting landmarks or characteristics from an image of the subject's face.For example, an algorithm can analyze the relative position, size and / or shape of the eyes, nose, cheekbones and jaw. These features are then used to search for other images with matching functions. Other algorithms normalize a gallery of face images and then compress the face data, only saving the data in the image that is useful for face recognition. Next, a probe image is compared to the face data. One of the first successful systems is based on techniques of combination of templates applied to a set of prominent facial features, providing a kind of representation of the compressed face.Recognition algorithms can be divided into two main approaches, geometric, which analyzes distinctive features, or photometric, which is a statistical approach that distills an image into values and compares values with templates to eliminate variations.
 Popular recognition algorithms include principal component analysis using proprietary faces, linear discriminant analysis, matching of elastic hand plots using the Fisherface algorithm, the hidden Markov model, multiline subspace learning using tensor representation and link pairing dynamic motivated by neurons. Three-dimensional recognitionThe three-dimensional facial recognition technique uses 3D sensors to capture information about the shape of a face. This information is used to identify the distinctive features on the surface of a face, such as the outline of the eye, nose and chin sockets. One advantage of facial recognition in 3D is that it is not affected by changes in lighting like other techniques. You can also identify a face from a range of viewing angles, including a profile view. The three-dimensional data points of a face greatly improve the accuracy of facial recognition. 3D research is reinforced by the development of sophisticated sensors that do a better job of capturing images of 3D faces.The sensors work by projecting structured light on the face. Up to a dozen or more of these image sensors can be placed on the same CMOS chip; Each sensor captures a different part of the spectrum .... Even a perfect 3D combination technique could be sensitive to expressions. For that goal, a Technion group applied metric geometry tools to treat expressions such as isometries. A new method is to introduce a way to capture a 3D image using three tracking cameras that point to different angles; a camera will be pointing to the front of the subject, the second to one side and the third to an angle.All these cameras will work together to be able to follow the face of a subject in real time and be able to detect and recognize. Skin texture analysis Another emerging trend uses the visual details of the mask, as captured in standard scanned or scanned images. This technique, called skin texture analysis, converts the lines, patterns and unique points apparent in a person's skin into a mathematical space. Tests have shown that with the addition of skin texture analysis, face recognition performance can increase from 20 to 25 percent. Thermal camerasA different way of taking input data for face recognition is through the use of thermal cameras, using this procedure the cameras will only detect the shape of the head and ignore the subject's accessories, such as glasses, hats or makeup. One problem with the use of thermal images for face recognition is that the databases for face recognition are limited. Diego Socolinsky and Andrea Selinger (2004) investigate the use of thermal facial recognition in real life and the operating scenarios, and at the same time create a new database of images of thermal faces.The research uses low-resolution, low-sensitivity ferroelectric electrical sensors that are capable of acquiring long-wave thermal infrared (LWIR). The results show that a fusion of LWIR and regular visual cameras has the best results in outdoor probes. Indoor results show that the visual has 97.05% accuracy, while LWIR has 93.93% and the Fusion has 98.40%, however, on the outside, the visual has 67.06 %, the LWIR 83.03% and the merger 89.02%. The study used 240 subjects during the 10-week period to create the new database. The data was collected on sunny, rainy and cloudy days.
Popular recognition algorithms include principal component analysis using proprietary faces, linear discriminant analysis, matching of elastic hand plots using the Fisherface algorithm, the hidden Markov model, multiline subspace learning using tensor representation and link pairing dynamic motivated by neurons. Three-dimensional recognitionThe three-dimensional facial recognition technique uses 3D sensors to capture information about the shape of a face. This information is used to identify the distinctive features on the surface of a face, such as the outline of the eye, nose and chin sockets. One advantage of facial recognition in 3D is that it is not affected by changes in lighting like other techniques. You can also identify a face from a range of viewing angles, including a profile view. The three-dimensional data points of a face greatly improve the accuracy of facial recognition. 3D research is reinforced by the development of sophisticated sensors that do a better job of capturing images of 3D faces.The sensors work by projecting structured light on the face. Up to a dozen or more of these image sensors can be placed on the same CMOS chip; Each sensor captures a different part of the spectrum .... Even a perfect 3D combination technique could be sensitive to expressions. For that goal, a Technion group applied metric geometry tools to treat expressions such as isometries. A new method is to introduce a way to capture a 3D image using three tracking cameras that point to different angles; a camera will be pointing to the front of the subject, the second to one side and the third to an angle.All these cameras will work together to be able to follow the face of a subject in real time and be able to detect and recognize. Skin texture analysis Another emerging trend uses the visual details of the mask, as captured in standard scanned or scanned images. This technique, called skin texture analysis, converts the lines, patterns and unique points apparent in a person's skin into a mathematical space. Tests have shown that with the addition of skin texture analysis, face recognition performance can increase from 20 to 25 percent. Thermal camerasA different way of taking input data for face recognition is through the use of thermal cameras, using this procedure the cameras will only detect the shape of the head and ignore the subject's accessories, such as glasses, hats or makeup. One problem with the use of thermal images for face recognition is that the databases for face recognition are limited. Diego Socolinsky and Andrea Selinger (2004) investigate the use of thermal facial recognition in real life and the operating scenarios, and at the same time create a new database of images of thermal faces.The research uses low-resolution, low-sensitivity ferroelectric electrical sensors that are capable of acquiring long-wave thermal infrared (LWIR). The results show that a fusion of LWIR and regular visual cameras has the best results in outdoor probes. Indoor results show that the visual has 97.05% accuracy, while LWIR has 93.93% and the Fusion has 98.40%, however, on the outside, the visual has 67.06 %, the LWIR 83.03% and the merger 89.02%. The study used 240 subjects during the 10-week period to create the new database. The data was collected on sunny, rainy and cloudy days.
 Popular recognition algorithms include principal component analysis using proprietary faces, linear discriminant analysis, matching of elastic hand plots using the Fisherface algorithm, the hidden Markov model, multiline subspace learning using tensor representation and link pairing dynamic motivated by neurons. Three-dimensional recognitionThe three-dimensional facial recognition technique uses 3D sensors to capture information about the shape of a face. This information is used to identify the distinctive features on the surface of a face, such as the outline of the eye, nose and chin sockets. One advantage of facial recognition in 3D is that it is not affected by changes in lighting like other techniques. You can also identify a face from a range of viewing angles, including a profile view. The three-dimensional data points of a face greatly improve the accuracy of facial recognition. 3D research is reinforced by the development of sophisticated sensors that do a better job of capturing images of 3D faces.The sensors work by projecting structured light on the face. Up to a dozen or more of these image sensors can be placed on the same CMOS chip; Each sensor captures a different part of the spectrum .... Even a perfect 3D combination technique could be sensitive to expressions. For that goal, a Technion group applied metric geometry tools to treat expressions such as isometries. A new method is to introduce a way to capture a 3D image using three tracking cameras that point to different angles; a camera will be pointing to the front of the subject, the second to one side and the third to an angle.All these cameras will work together to be able to follow the face of a subject in real time and be able to detect and recognize. Skin texture analysis Another emerging trend uses the visual details of the mask, as captured in standard scanned or scanned images. This technique, called skin texture analysis, converts the lines, patterns and unique points apparent in a person's skin into a mathematical space. Tests have shown that with the addition of skin texture analysis, face recognition performance can increase from 20 to 25 percent. Thermal camerasA different way of taking input data for face recognition is through the use of thermal cameras, using this procedure the cameras will only detect the shape of the head and ignore the subject's accessories, such as glasses, hats or makeup. One problem with the use of thermal images for face recognition is that the databases for face recognition are limited. Diego Socolinsky and Andrea Selinger (2004) investigate the use of thermal facial recognition in real life and the operating scenarios, and at the same time create a new database of images of thermal faces.The research uses low-resolution, low-sensitivity ferroelectric electrical sensors that are capable of acquiring long-wave thermal infrared (LWIR). The results show that a fusion of LWIR and regular visual cameras has the best results in outdoor probes. Indoor results show that the visual has 97.05% accuracy, while LWIR has 93.93% and the Fusion has 98.40%, however, on the outside, the visual has 67.06 %, the LWIR 83.03% and the merger 89.02%. The study used 240 subjects during the 10-week period to create the new database. The data was collected on sunny, rainy and cloudy days.
Popular recognition algorithms include principal component analysis using proprietary faces, linear discriminant analysis, matching of elastic hand plots using the Fisherface algorithm, the hidden Markov model, multiline subspace learning using tensor representation and link pairing dynamic motivated by neurons. Three-dimensional recognitionThe three-dimensional facial recognition technique uses 3D sensors to capture information about the shape of a face. This information is used to identify the distinctive features on the surface of a face, such as the outline of the eye, nose and chin sockets. One advantage of facial recognition in 3D is that it is not affected by changes in lighting like other techniques. You can also identify a face from a range of viewing angles, including a profile view. The three-dimensional data points of a face greatly improve the accuracy of facial recognition. 3D research is reinforced by the development of sophisticated sensors that do a better job of capturing images of 3D faces.The sensors work by projecting structured light on the face. Up to a dozen or more of these image sensors can be placed on the same CMOS chip; Each sensor captures a different part of the spectrum .... Even a perfect 3D combination technique could be sensitive to expressions. For that goal, a Technion group applied metric geometry tools to treat expressions such as isometries. A new method is to introduce a way to capture a 3D image using three tracking cameras that point to different angles; a camera will be pointing to the front of the subject, the second to one side and the third to an angle.All these cameras will work together to be able to follow the face of a subject in real time and be able to detect and recognize. Skin texture analysis Another emerging trend uses the visual details of the mask, as captured in standard scanned or scanned images. This technique, called skin texture analysis, converts the lines, patterns and unique points apparent in a person's skin into a mathematical space. Tests have shown that with the addition of skin texture analysis, face recognition performance can increase from 20 to 25 percent. Thermal camerasA different way of taking input data for face recognition is through the use of thermal cameras, using this procedure the cameras will only detect the shape of the head and ignore the subject's accessories, such as glasses, hats or makeup. One problem with the use of thermal images for face recognition is that the databases for face recognition are limited. Diego Socolinsky and Andrea Selinger (2004) investigate the use of thermal facial recognition in real life and the operating scenarios, and at the same time create a new database of images of thermal faces.The research uses low-resolution, low-sensitivity ferroelectric electrical sensors that are capable of acquiring long-wave thermal infrared (LWIR). The results show that a fusion of LWIR and regular visual cameras has the best results in outdoor probes. Indoor results show that the visual has 97.05% accuracy, while LWIR has 93.93% and the Fusion has 98.40%, however, on the outside, the visual has 67.06 %, the LWIR 83.03% and the merger 89.02%. The study used 240 subjects during the 10-week period to create the new database. The data was collected on sunny, rainy and cloudy days.
Biometrides
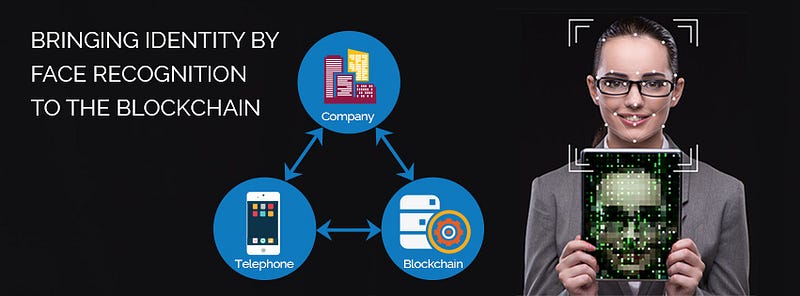
a new platform built to facilitate the identification of users of automotive devices. at the same time as a platform that can solve identity problems in blockchain
The Biometrids platform allows people to identify themselves with other people through facial recognition installed on their phones. Using a distributed ledger that does not change, everyone in the chain is unique. A face means an ID, and each ID is unique. If you are registered in that chain once, you will never be able to manipulate that ID again or copy that ID. This will prevent identity theft and fraud, and will also ensure that users are who they say.
a new platform built to facilitate the identification of users of automotive devices. at the same time as a platform that can solve identity problems in blockchain
The Biometrids platform allows people to identify themselves with other people through facial recognition installed on their phones. Using a distributed ledger that does not change, everyone in the chain is unique. A face means an ID, and each ID is unique. If you are registered in that chain once, you will never be able to manipulate that ID again or copy that ID. This will prevent identity theft and fraud, and will also ensure that users are who they say.

Chip sales https://biometrids.io/ The name of the token will be IDS. There will be a total of 100,000,000 IDS.
5% will be sold in pre-ICO.
5% will be for rewards and advisors.
70% will be sold in crowdsale.
10% will be for the team.
10% will be for the foundation. Pre-ICO will run for a week and the price will be 910 IDS / 1eth. The crowdsale will run for four weeks and the prices will be:
Week 1: 665 IDS / 1eth
Week 2: 550 IDS / 1eth
Week 3: 500 IDS / 1eth
Week 4: 450 IDS / 1eth Pre-Ico and crowdsale will run to date of completion, or until all coins are sold.10% for the team and 10% for the foundation will be under lock and key for three years. Each currency not sold during the ICO will be blocked for five years. After five years, they will be sold to the first investors in a private fundraising campaign. They will not be sold in exchanges.
For More Information :
ICO: https://biometrids.io/
TELEGRAM: https://t.me/joinchat/E-BNGBDaHcasMMJOlsEPmw
FACEBOOK: https://web.facebook.com/Biometrids-1603692473026252/?_rdc=1&_rdr
TWITTER: https://twitter.com/biometrids
BOUNTY: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=2345586.0
TELEGRAM: https://t.me/joinchat/E-BNGBDaHcasMMJOlsEPmw
FACEBOOK: https://web.facebook.com/Biometrids-1603692473026252/?_rdc=1&_rdr
TWITTER: https://twitter.com/biometrids
BOUNTY: https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=2345586.0
Profile bitcointalk : https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?action=profile
ETH : 0xd3c9e8608103cf2c8b153c8d7404fc5b563d9470

Komentar
Posting Komentar